Health and Safety

Health and Safety is one of enterprise materiality that important to SCG and integrated into all business units long term plan under supervision by Sustainable Development Committee, SCG that consisted of Workplace Safety Committee and Transportation Safety Committee with a role to determine strategies and monitor regularly.
SCG announce SCG Safety Framework and been supervised by Safety Performance Assessment Program, SPAP since 2007 in all operations. We continue to enhance the standard for safety supervision and control to the present to eventually achieve the goal of Injury and Illness Free sustainably.
Target in 2024
- Zero fatality of employees and contractors.
- Zero Lost time injury frequency rate of employees and contractors.
- Zero occupational illness frequency rate of employees.
- All companies under SCG pass the Safety Performance Assessment Program (SPAP) at the Standard level and higher.
Strategy
1. Elevate the implementation of the Occupational health and safety management system, standards, Life Saving Rules, and transportation safety to ensure effectiveness both in Thailand and Abroad.
2. Foster participation and quality promotion in risk identification and management by oneself to foster an organization-wide safety culture.
3. Apply the Safety Performance Management System (PMS) to ensure the actual implementation of safety policies and establish shared goals for use in safety performance assessment.
4. Utilize digital technology to improve operational efficiency and support business growth to reduce risks of accidents, injuries, and occupational illnesses and diseases.
5. Communicate lessons learned from incidents, promptly and inclusively, to expand on rectification, and prevention to avoid recurrence, as well as review safety measures to make sure they are proportionate to the risk and up to speed with changes in respective business.
Management
- The Workplace Safety Committee and the Transportation Safety Committee establish policies, strategies, short-, medium-, and long-term action plans, targets, and indicators. They actively monitor the achievement of targets, oversee plan implementation, and analyze outcomes to continuously enhance effectiveness.
- Report occupational health and safety performance to the top management and the Board of Directors on a quarterly basis.
- Establish mechanisms for regular self-auditing to encourage ownership and self-discipline.
- Foster a collaborative management network, develop experts in each business unit, and enrich the knowledge and capabilities of employees and contractors in order to bring about the exchange of knowledge and technology for collaborative risk management.
Key Activities
Workplace Safety
SCG Safety Framework
SCG Safety Framework consisted of 13 elements as follows.
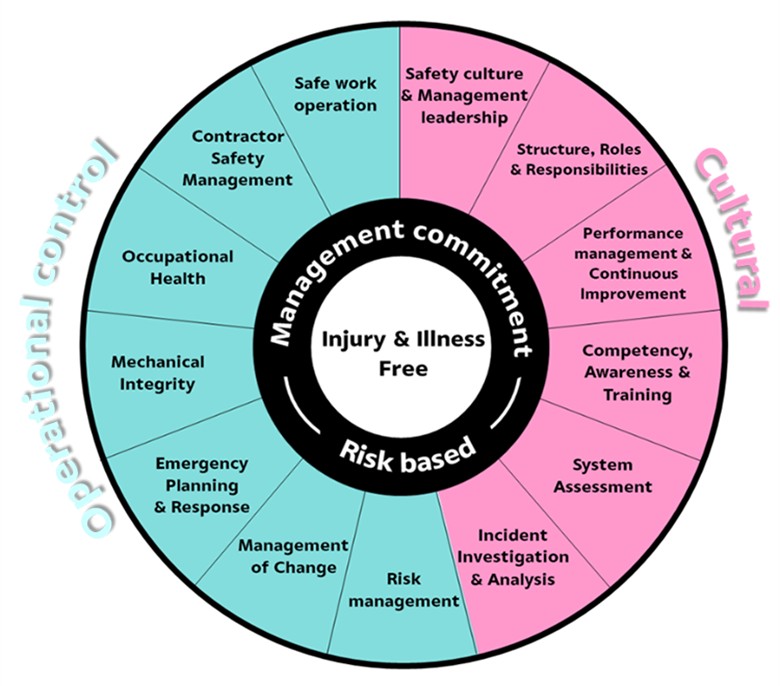
To achieve the ultimate goal for Injury & Illness Free, every companies must comply with the requirements of SCG Safety Framework.
Element 1: Safety Culture & Management Leadership
Encourage occupational health and safety as a core value and the first priority of work to everyone. Leaders have the important roles on Management Leadership and provide concrete supporting that lead to Safety Culture of SCG according to SCG Safety Culture & Management Leadership Guideline.
Element 2: Structure, Roles & Responsibilities
All employee and contractor in all levels have been informed and perform their duties and responsibilities on occupational health and safety clearly.
Element 3: Performance management & Continuous improvement
To ensure the concrete implementation and continuous improvement of Occupational Health and Safety Management System by setting medium term plan and action plan, leading and lagging key performance indicators and deployed at the appropriate personnel/ department level so that they may be used to measure, monitoring performance at the personnel/department level (Performance Management System; PMS).
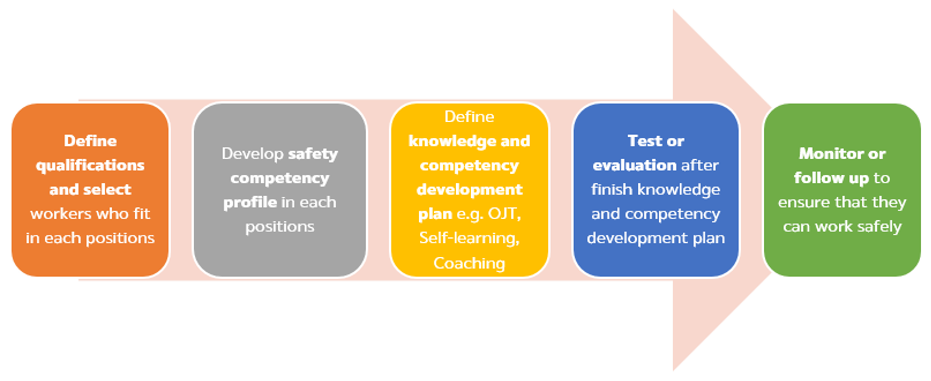
Element 4: Competency, Awareness & Training
Knowledge and competency development and OHS training provided to employees and other relevant parties to raise awareness and reduce operational health and safety incidents with the following actions.
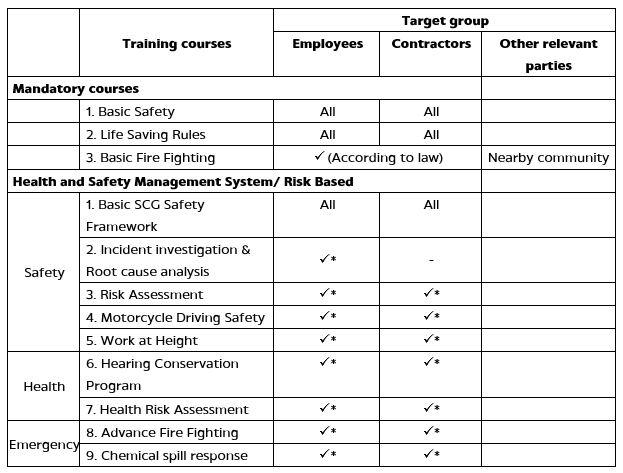
Health and Safety training programs for employees/ contractors and/ or other relevant parties
Element 5: System Assessment
To assess the compliance and efficiency of Occupational Health and Safety Management System then define corrective and preventive actions for continuous improvement. Every companies must conduct the internal inspections/ audit which covers SCG Safety Framework all elements and report through SPAP Self-declaration every year and the external audit by 3rd Party of compliance audit at least every 2 years.
Element 6: Incident Investigation & Analysis
Focus on effective incidents prevention including reporting and investigation that cover work-related injury, occupational illness and disease, emergency, off the job and near miss by participation of all workers at all level according to SCG Safety Incident Information and Reporting Standard and SCG Incident Investigation & Analysis Standard which is the procedures to investigate work-related injuries, ill health, diseases and incidents.
Element 7: Risk Management
To identify OHS risk and hazards assessments in order to truly achieve injury and illness free according to hazard identification and risk assessment procedure/ standard what could cause harm in the workplace to differentiate level of risks that lead to elimination, reduction and control hazards or risks into acceptable level in every activity, processes areas and products. Summarize, compile, and analyze of the recommendations and results from risk assessment to system improvement and from risk management such as the number of risks at each level, analysis of type and characteristics of hazards from assessment, or analysis of the results of executing the specified risk management measures at the company level, for prioritization and integration of action plans with quantified targets to address those risks and evaluation of the progress against the target for further improvement.

Element 8: Management of Change
Impact on Occupational Health and Safety for new project or any change in technology and facility has been analyze including Pre Start Up Safety Review according to SCG Management of Change Standard.
Element 9: Emergency Planning and Response
To ensure that all companies have the availability of resources and can manage the resources needed to response and manage emergency related to the company’s risks such as fire, explosion, chemical spills. Including earthquakes, floods, tsunamis, etc. Then develop emergency planning and respond procedures and emergency plans, provide training and emergency drill at least once a year. The integration of actions to prepare for and respond to emergency situations according to SCG Emergency Planning and Response Standard.
Element 10: Mechanical Integrity
The reliability of the machines, tools and equipment used in the operation that can cause severe damage to life, property as well as the disruption of the production process along the production line or interrupted production in other sections as well according to SCG Mechanical integrity standard.
Element 11: Occupational Health
Health Management System with an integration of occupational health with industrial hygiene. Health Risk Assessment is carried out lead to determination of measures for risk mitigation or action plans, Industrial hygiene monitoring plan, health surveillance that related to health hazards. Then, the information gained from this assessment was analyzed in coordination with occupational medicine doctors to investigate any abnormal signs that may lead to occupational illness and disease. Moreover, the information was used in examining health condition before assigning a suitable task to them and also used in setting up a holistic health care program for improving a higher quality of life of workers according to SCG Health Risk Assessment and Risk Management Standard, SCG Health Surveillance Standard and SCG Industrial Hygiene Monitoring Standard. Monitoring and evaluation of progress in reducing/ preventing health issues/ risks against targets regularly.
Element 12: Contractor Safety Management
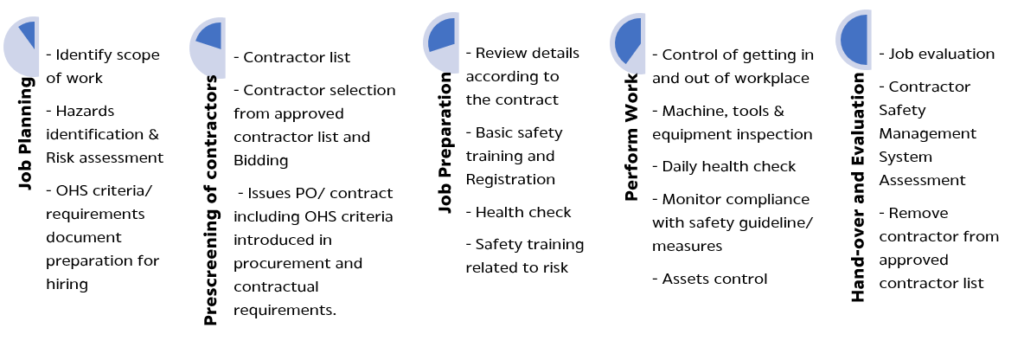
Contractor’s safety poses a significant risk and target for SCG’s sustainable development strategy. Training and communication are emphasized to create knowledge, understanding especially safety awareness and reduce safety risks among contractors, in order to truly achieve injury and illness free according to SCG Safety Management for Service Solutions Standard and SCG Contractor Safety Management Standard that consisted of 5 following steps
- Job planning to identify scope of work, conduct hazards identification & risk assessment and prepare OHS criteria/ requirements document for hiring. Compliance with safety guidelines included in contractual agreements
- Prescreening of contractors to ensure that only competent and reputable contractors are selected. This may involve evaluating their safety records, certifications, training programs, and previous experience.
- Job Preparation Provide comprehensive orientation and training to contractors. This should include an overview of the site-specific hazards and any specific safety requirements.
- Perform Work to supervise contractors during their work to ensure they are following safety procedures and standards
- Hand-over and Evaluation to evaluate contractor safety performance regularly and provide feedback. Recognize and reward contractors for excellent safety performance and address any deficiencies promptly.
Targets and result regarding contractor and supplier safety
| Targets regarding contractor safety | Result 2022 |
|---|---|
| 100% of operation contractors certified under contractor safety management | 89% |
| 100% of major carriers certified under Fleet Carrier Standards | 100% |
| 100% of contractors and suppliers with procurement spending of over 1 million bath passed ESG risk assessment | 100% |
| 95% of contractors and suppliers demonstrated intent to comply with SCG Supplier Code of Conduct | 94% |
Read more detail on key actions for contractors and suppliers management in SD Report 2023, Supplier Governance and Enhance Towards Sustainability.
Element 13: Safe Work Operation
To support occupational health and safety risk management to control and/ or reduce the likelihoods of risks. In the present, SCG developed corporate standards that being applied to all companies such as.
- Electrical Safety
- Energy Isolation and Lockout Tagout System
- Work Permit System
- Lifting Safety
- Occupational Safety in Confined Space
- Work at High Elevation
- Machinery Safeguarding
- Chemical Management etc.
Safety Performance Assessment Program (SPAP)
Target: All companies under SCG pass the Safety Performance Assessment Program (SPAP) at the Standard level or higher.
SPAP Self-declaration Result in 2023 compare 2022


In 2023, 100% of SCG’s plants/ subsidiaries in Thailand and Abroad implemented and passed SPAP assessment, the result of the final SPAP Self-declaration of Thailand operations in Excellence level is 7%, Advance level is 16%, Standard level is 66% and Awareness level is 11%. For Abroad operation in Standard level is 72% and Awareness level is 28% respectively.
Moreover, 90% subsidiaries under business units of SCG have been external certified from independent external verification of health, safety and well-being such as OHSAS/ TIS 18001/ ISO 45001
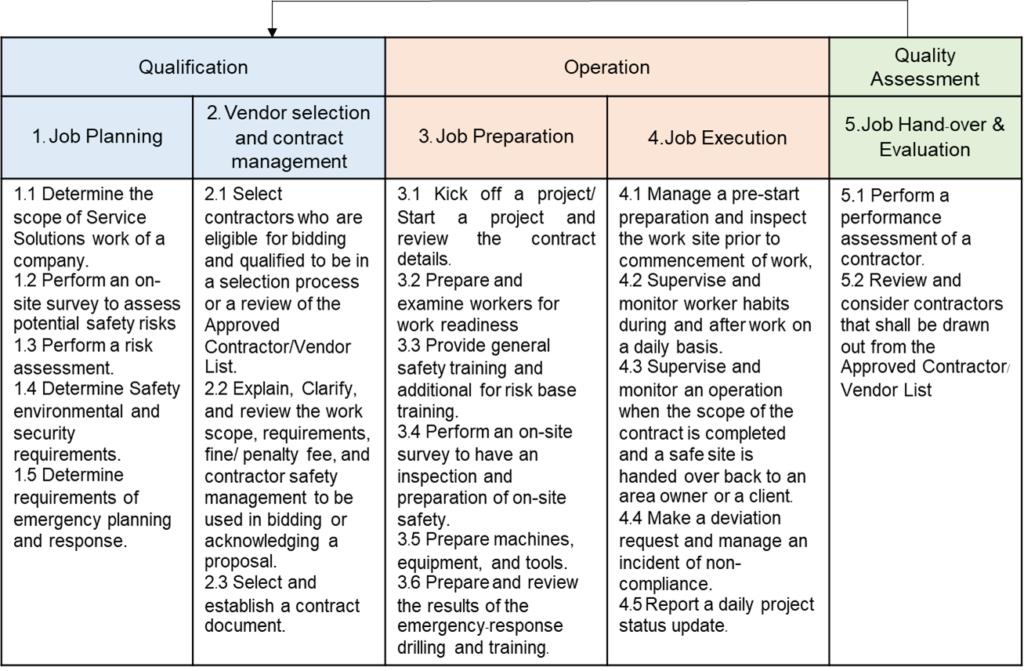
Safety Management for Service Solutions Standard
Accompanying the expansion of service solutions businesses are the increasing number of contractors for Accompanying the expansion of service solutions businesses are the increasing number of contractors for such businesses and greater risks of accidents. In 2022, SCG introduced the Safety Management for Service Solutions Standard, And in 2023 expanded and co-developed safety management for solar business. The standard consists of three management components: 1) Qualification, 2) Operation, and 3) Quality Assessment. There are 5 steps with detail as follows.
- Job Planning
- Vendor selection and contract management
- Job Preparation
- Job Execution
- Job Hand-over & Evaluation
9 Life Saving Rules
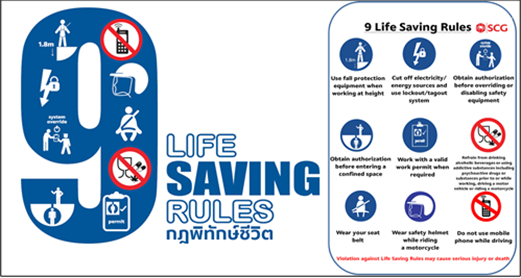
According to continuous stringent monitoring, controlling, communication and developing Safe work standards to reduce unsafe behaviors to prevent Life Saving Rules violations. In 2023, the overall violation decreases 52.38% from 2022 and the majority of the violations were.
- 70.00% of all violations from No. 6: Refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages or using addictive substances including psychoactive drugs or substances prior to or while working, driving a motor vehicle or riding a motorcycle.
- 6.15% of all violations from No. 7: Refrain from wearing a safety belt when traveling in a motor vehicle.
- 5.38% of all violations from No. 1: Refrain from using fall protection equipment when working outside a protective environment where one can fall from height over 1.8 meters.
Travelling and Transportation Safety
SCG still strives to reduce injuries and fatalities from transportation accidents to zero by 2023, including accidents during operation hours, mainly caused by risky behaviors and a lack of operational discipline, and off-the-job accidents attributable primarily to motorcycle accidents. SCG has taken the following key actions:
- Promoting Operational Discipline (OD) to all business units and carriers, setting up assessments and developing plans for safety rectification with regular monitoring and follow-up.
- Controlling the working and rest hours of drivers to reduce the risk of accidents caused by fatigue.
- Establishing an accident investigation committee consisting of representatives from each business unit to analyze root causes and prevent the recurrence of incidents. Sharing lessons learned from accidents between business units.
- Expanding Safe Travel and Transport Measures abroad through the launch of Goods Transportation Safety initiatives in Vietnam, Indonesia, Laos, and Cambodia. Additionally, conducting visits to transport carriers in Laos and Cambodia to provide advice and enhance safety performance.
- Implementing an off-the-job accident-reduction plan, including safe driving practices to demonstrate care and adopting safety guidelines to apply even outside of working hours.
SCG also develops technologies and systems for tracking and monitoring the driving behavior of drivers, such as:
- Logistics Command Center (LCC): A 24-hour AI-powered command center that controls driver behaviors, including facilitating fleet scheduling and route planning.
- Advanced Driving Assistance System (ADAS) and Driver Monitoring System (DMS): These systems, in conjunction with two-way GPS cameras, monitor driver behavior. Additionally, truck driver fatigue management is implemented to control work hours, rest hours, and help reduce fatigue-induced accidents.Top of Form
SCG Occupational Health and Safety Policy
Workplace and Transportation Safety Risks Management
Process Safety Management
Occupational Health Management
OHS Training Courses
Independent External Verification (ISO45001)
Health and Safety Performance
SCG Goods Transportation Safety Standard
Incident investigation Standard
Emergency preparedness procedure
Health Risk Assessment and Risk Management procedure